What is Blockchain?: A Comprehensive Exploration Blockchain, the revolutionary technology that underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has emerged as a transformative force across various industries. In this in-depth exploration, we’ll unravel the intricacies of blockchain, examining its origins, underlying principles, applications, and the potential it holds for reshaping the future of digital transactions.
Genesis of Blockchain
The roots of blockchain can be traced back to a 2008 whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” authored by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto. This groundbreaking document introduced the concept of a decentralized, distributed ledger as the foundation for a new form of digital currency – What is Blockchain?: A Comprehensive Exploration Bitcoin. Blockchain was conceived as the underlying technology that would bring transparency, security, and decentralization to financial transactions.

Core Principles of Blockchain
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized model, where each participant in the network (node) maintains a copy of the entire ledger. This ensures transparency and mitigates the risk of a single point of failure.
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the entire blockchain network, enhancing security and resilience.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the public ledger and can be accessed by network participants, fostering trust and accountability.
- Immutability: Once a block is added to the chain, it is nearly impossible to alter previous blocks, ensuring the integrity of the entire transaction history.
- Consensus Mechanism: Blockchain relies on a consensus algorithm along nodes to validate and agree on the state of the ledger, ensuring uniformity across the network.
How Blockchain Works
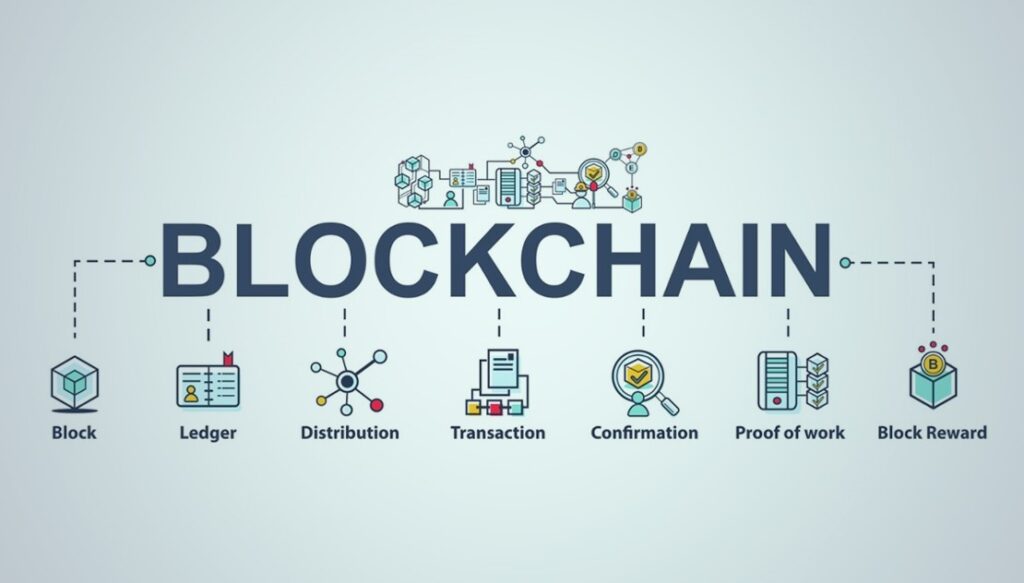
Blockchain operates through a series of interconnected blocks, each containing a list of transactions. When a new transaction occurs, it is grouped with others into a block, which is then added to the existing chain. Each block is linked to the previous one through a cryptographic hash, creating a continuous and unchangeable chain of blocks.
The consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work (used in Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake, plays a crucial role in validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the ledger. These mechanisms ensure that participants reach an agreement before a new block is added, preventing fraud or malicious activities.
Beyond Cryptocurrencies: Diverse Applications of Blockchain
While blockchain gained prominence as the technology behind cryptocurrencies, its versatility extends far beyond the realm of digital coins. Industries across the spectrum are exploring innovative applications.
- Blockchain is disrupting traditional financial systems with faster, more transparent, and cost-effective transactions. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with coded terms, automate complex financial processes.
- Blockchain enhances traceability and reduces fraud in supply chains by recording every step of a product’s journey. This ensures authenticity and transparency from manufacturing to delivery.
- Patient records, pharmaceutical supply chains, and clinical trials can benefit from blockchain, ensuring secure, interoperable, and transparent data sharing while protecting patient privacy.
- Property transactions and land registries can be streamlined and made more secure through blockchain, reducing fraud and ensuring transparent ownership records.
- Beyond financial applications, smart contracts automate and enforce the execution of predefined terms in various fields, from insurance and legal agreements to entertainment and gaming.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the potential of blockchain is immense, it faces challenges such as scalability, energy consumption (especially in Proof of Work systems), and regulatory uncertainties. As technology evolves, solutions like sharding, consensus algorithm improvements, and regulatory frameworks are being explored to address these issues.
The future of blockchain holds promises of increased adoption and integration into everyday life. As more industries recognize the benefits of decentralized, secure, What is Blockchain?: A Comprehensive Exploration and transparent systems, blockchain is poised to reshape the foundations of how we transact, interact, and trust in the digital age.
In conclusion, blockchain is a transformative technology that transcends its origins in cryptocurrency. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature has the potential to revolutionize industries, streamline processes, and foster trust in an increasingly digital world. As blockchain continues to evolve and find new applications, its impact on the way we conduct business, secure data, and interact with technology is likely to be profound and far-reaching.
1 thought on “What is Blockchain?: A Comprehensive Exploration”